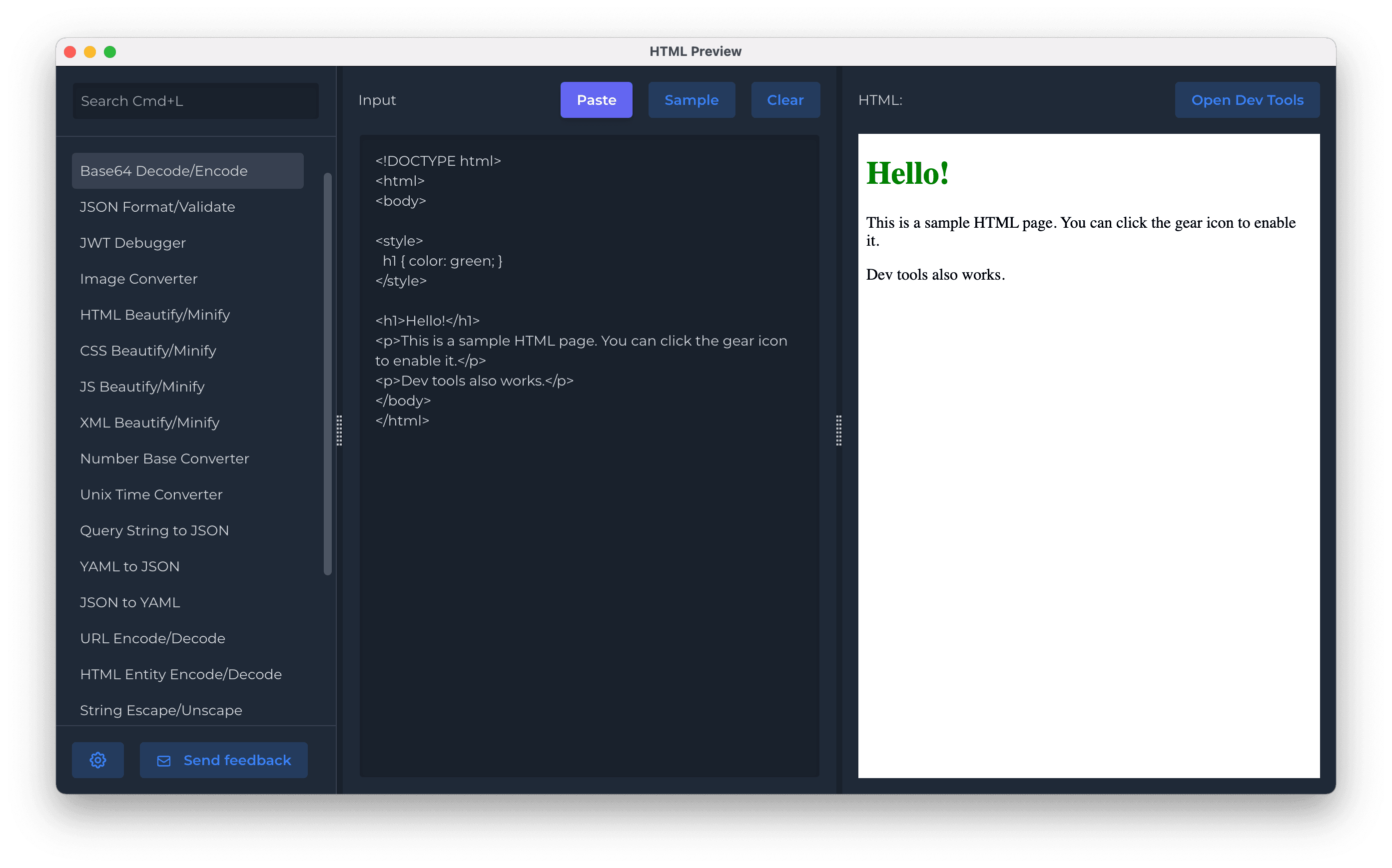
HTML preview
Completely offline
Tools to do exactly what it says: Preview you html without creating html file. Just paste code and quickly get output
Download for Windows

What is HTML?
The HyperText Markup Language, or HTML is the standard markup language for documents designed to be displayed in a web browser. It can be assisted by technologies such as Cascading Style Sheets (CSS) and scripting languages such as JavaScript.Web browsers receive HTML documents from a web server or from local storage and render the documents into multimedia web pages. HTML describes the structure of a web page semantically and originally included cues for the appearance of the document.
HTML elements are the building blocks of HTML pages. With HTML constructs, images and other objects such as interactive forms may be embedded into the rendered page. HTML provides a means to create structured documents by denoting structural semantics for text such as headings, paragraphs, lists, links, quotes and other items. HTML elements are delineated by tags, written using angle brackets. Tags such as <img /> and <input /> directly introduce content into the page. Other tags such as <p> surround and provide information about document text and may include other tags as sub-elements. Browsers do not display the HTML tags, but use them to interpret the content of the page.
More on Wiki
Download for Windows